Chili summer management
First, fertilizer water management matters needing attention:
Moisture management: watering should be uniform, avoid dry and wet, avoid drought and rain, watering in time after setting. After one week, the seedling water is poured, and after each watering, the method of alternate irrigation is used. After the seedling water is slowed down, the first layer of water is poured when the first layer is about 2 cm long, and water is poured once a week according to the situation. During the ripening period of the fruit, the watering should be controlled, and the water in the field should be removed in time. The irrigation should be carried out after the cold weather in the afternoon, and it is raining after the irrigation.
Topdressing management: After planting, it is necessary to grab the sunny day to apply for the seedling fertilizer. Each dose should not be too much or too thick, otherwise it will cause a long delay and delay the flowering result. After the first and second layers of fruit are applied, it is necessary to apply more fertilizer to promote fruit growth. After the fruit is harvested, the soil is required to have sufficient fertilizer to allow the plants to grow normally and produce results. If the soil is not dry before the watering, the leaves and dead plants will be quite common, especially during the period from the ups and downs to the autumn. Therefore, when irrigating, the irrigation time must be determined according to the weather forecast. The depth of irrigation should not exceed three-quarters of the ditch, and it should be carried out at night or in the early morning, and the emergency irrigation should be urgently discharged. (Using municipal waste, industrial waste residue and organic fertilizer that has not been harmlessly treated should not be used in production. Appropriate application of biological fertilizer before rain or before watering can help loosen the activated soil and prevent root pathogens)
(6) Occurrence and prevention of falling flowers, fruit falling, and defoliation: The flowering, fruit falling and deciduous phenomena of pepper have a great influence on the yield. The flowering rate is generally 20% to 40%, the fruit drop rate is 5% to 10%, the temperature is too high or too low, and the pollination and poor fertilization of pepper are the main causes of falling flowers. The main reason for falling flowers in the early spring: low temperature and rain, insufficient light, affecting the normal conduct of pollination and fertilization. On the other hand, poor cultivation and management, such as excessive application of fertilization, plant length, planting too dense, poor ventilation and light or nitrogen, phosphorus deficiency, etc., will cause falling flowers, fruit drop. Soil moisture imbalance, excessive humidity, excessive or smear, hinder root growth, causing fruit drop and defoliation. In addition, some diseases can also be caused. At this time, the 1500 times solution of Naduobao should be sprayed before and after the flower to prevent falling flowers, fruit drop and poor pollination. There are also plant adjustments, the lateral branches of the base are wiped out as soon as possible, and the old and yellow diseased leaves are removed in time. If the density is too large, a right is left in the two rights issued to control the growth.

Second, pepper pest control technology
Pest control should be "prevention first, comprehensive prevention", based on agricultural control, actively apply physical and biological control methods, chemical control should master the correct application method, reduce the amount of chemical pesticides, implement pesticide safety standards, and make pepper fruits The pesticide residue in the medium does not exceed the standard.
1. Agricultural control: selection of pest-resistant varieties; cultivation of age-appropriate seedlings; strict rotation; high-mulch mulching cultivation; rational close planting, scientific fertilization, timely irrigation and drainage, cultivation of robust plants, and early closure of ridges (rows); Clean the pastoral, deep turn over the soil, reduce the source of overwintering insects; timely remove the diseased leaves, pests and diseases, timely remove the diseased plants, bring out the field or shed outdoor burning or deep burial.
2. Physical control: artificially remove pests and eggs, kill pests; yellow worms in the field to prevent cockroaches, whitefly, white larvae, sweet and sour liquid, black light to trap small tigers; sexual attractants to trap pests; incandescent lamps, High-pressure mercury lamp, frequency-vibration insecticidal lamp to trap the night moth pests; silver-gray film in the field or hanging silver-gray film strip to repel aphids, insect-proof nets to prevent insects (such as aphids, cotton bollworms, American scorpion flies) disease prevention (viral disease) Cultivation.
3. Biological control: protection and utilization of natural enemies, such as ladybugs, grasshoppers, and beetles, on the natural control of aphids; Trichogramma against cotton bollworms and tobacco budworms; using microbial preparations such as agricultural streptomycin to control pepper bacterial wilt and scab Disease, soft rot, leaf spot, and green worms control tobacco budworms.
4, disease and prevention
Pepper blight:
A Prevention: Ac (667m2) with 3 kg of copper sulfate applied to the ground, ploughed into the soil; found that the central diseased plant was immediately removed, disinfected with lime to spread the diseased plants, while spraying 75% chlorothalonil WP 600 Double solution or cyperidazole suspension 2000 times solution (trade name: Kejia, made in Japan) 1-2 times.
B Treatment: Spray the lower part of the plant and the surrounding surface with 500% of Reidomil Mn-Zn wettable powder 500 times, and spray with 75% chlorothalonil WP 600 times after 7 days. The two drugs are used alternately 1-2 times. Also available is 90% ethyl aluminum phosphate 500 times liquid or 69% Ank manganese zinc wettable powder 1000 times liquid, or 72.2% Plex aqueous solution 600 times liquid, or fluazinam 2000 times liquid (trade name: Fu Shuai, Sprayed in Japan), every 5-7 days, different chemicals are alternately controlled.
Capsicum virus disease:
A Early control of aphids: sprayed with 10% imidacloprid wettable powder 2000-4000 times spray.
B In the early stage of the disease, spray 20% virus A wettable powder 500 times solution, or 2% Ningnanmycin 200 times solution, or 1.5% phytopathogenic emulsion 1000 times solution, or èƒ èƒ Â· copper acetate (virus kill) 600 times solution , every 7-10 days, 3-4 times in a row
Capsicum anthracnose:
In the early stage of the disease, spray 70% thiophanate-methyl WP 600-800 times solution, or 80% anthrax defame WP 800 times solution, or 40% carbendazim suspension 600 times solution, or 75% chlorothalonil. Wet powder 800 times solution, once every 7-10 days, 2-3 times in a row.
5. Pests:
Tobacco budworm: The key is to seize the period from the peak of hatching to the age of 2, and the larvae have not been applied to the fruit. Can be used to kill cockroach (21% synergistic cyanoma emulsifiable concentrate) 1500-3000 times liquid + return 300 times, or 2.5% cyhalothrin emulsifiable concentrate (chlorofluorocyanate) 2000 times liquid + return 300 times. The above drugs are used interchangeably once every 10 days for 2-3 consecutive times. 2. 跗 line 螨 (tea 螨 or white spider)
The key to the prevention and treatment of chemical agents is to detect the early occurrence of coils (or 5% of the plant) in the field center. The focus of the spray is on the younger part of the plant, especially on the back of several top leaves. It can be used with 73% gram of emulsifiable concentrate 1000-1200 times liquid + return 300 times, or 35% chlorpyrifos 1000 times solution, or 20% oxazin thiophene 1000 times solution. It must be sprayed a second time within 3-5 days after the first spraying, the effect is good, and then sprayed once every 7 days, for 3 consecutive times.
Aphids: Mainly damage the leaves of plants, causing leaf deformities. It is necessary to prevent it in advance in production, and spray it 1-2 times with 500 times in advance; when it has a rate of 20%, use 10% imidacloprid 2000 times solution + return 300 times, or 50% sputum fog WP 2000- 3000 times liquid + 300 times return, or 50% malathion EC 1000 times solution, or 2.5% deltamethrin emulsifiable concentrate or 20% fast killing emulsifiable concentrate 2000-3000 times liquid spray control.
This article URL: Chili Summer Management
Sweet corn. The light green outer leaves of sweet corn are yellow grains, but also purple and yellow. The grains are small and round, the skin is thin and soft, tender, sweet and delicious.Contains carotene, zeaxanthin, with the effect of eye protection.
Sweet corn is most often boiled into soups. It is a favorite soup for children and adults, whether it is made into a clear corn soup with ribs or pureed with cream.
Corn is also a good choice for consumption during weight loss because of its high available energy. The metabolic energy of corn is 14.06 MJ/kg, with the highest being 15.06 MJ/kg, the highest of the cereal feeds. This is mainly due to the fact that there is very little crude fibre in corn, only 2%, while the nitrogen-free leachate is up to 72% and the digestibility is up to 90%; on the one hand, corn has a high crude fat content, between 3.5% and 4.5%.
So how do you cook a sweet corn?
1. Leave the leaves
If you strip the leaves off, the corn will lose nutrients and flavor when it cooks, so it's best to leave two thin leaves to make it easier to cook and have a nice aroma.
2. Soak
Soak the corn in cold water for 20 to 30 minutes before boiling, then boil it on high heat to give it a bit more chew.
3. Add salt
When the water is boiling, add a little salt to amplify the sweetness of the corn.
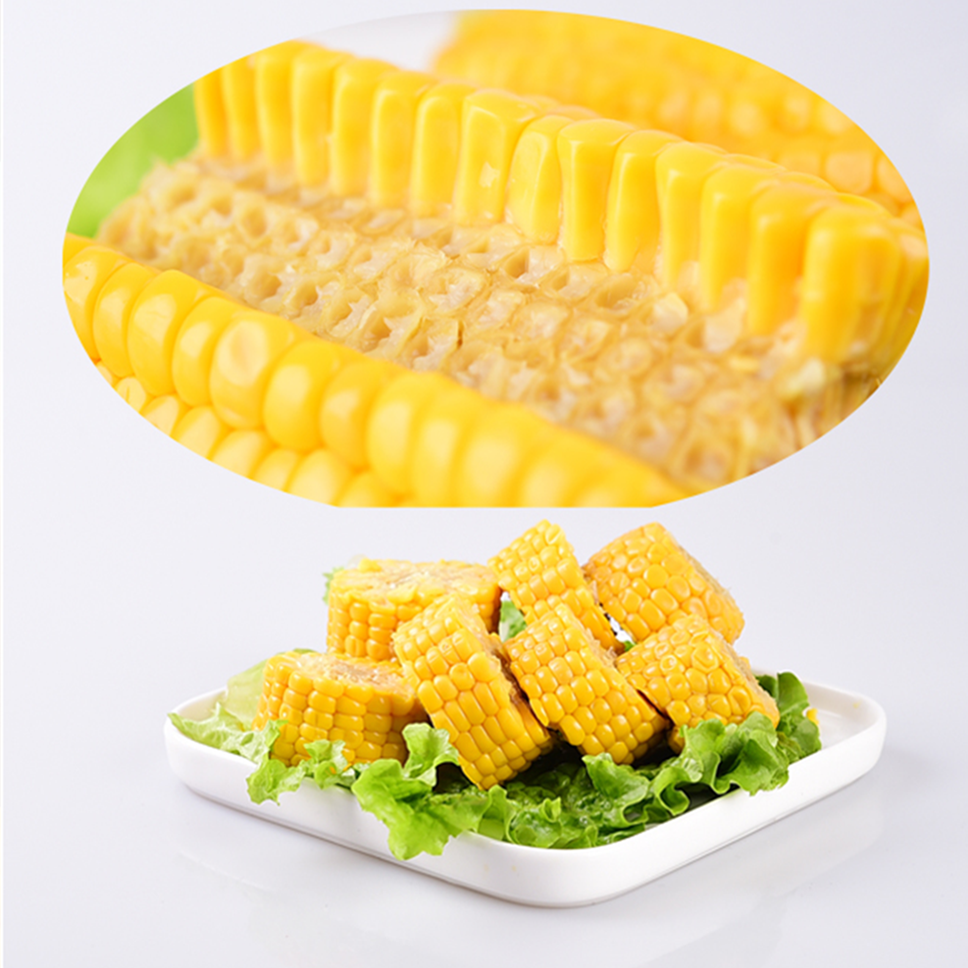

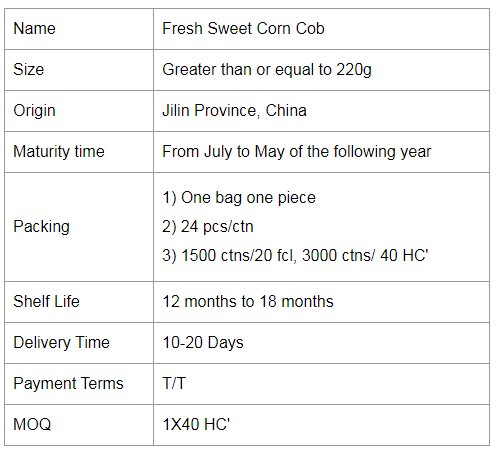
Corn Cob,Fresh Corn Cob,Ready Sweet Corn,Single Packed Sweet Corn Cob
Jilin Province Argricultural Sister-in-law Food Co., Ltd. , https://www.nscorn.com