Root mustard pest and disease control
First, the main diseases
The main disease that harms kohlrabi is the virus. The main source of poison is the turnip mosaic virus disease. Rhizoctonia seedlings infected with virus disease, faded green round spots appear on the leaves, heart veins. The late leaves showed pale green and yellowish green mottled or obvious mosaic symptoms, and the leaves shrank. After becoming a victim, the symptoms of heart and leaves are the same as those of seedlings. Severe foliar deformity, shrinkage, necrosis of leaf veins, dwarfing of plants, cessation of growth or death.
The virus can be used for wintering on seedlings and it can also be used for wintering on vegetables and field weeds. The virus is mainly transmitted by locusts.
Control methods: 1. Appropriate late sowing: Rhizospergia sown earlier than the appropriate late sowing is more susceptible to viral disease. It should be sown as late as possible without affecting the swelling of the roots. Root mustard is generally used for processing. Maturity has little impact on value sooner or later. Therefore, it is not necessary to sow seeds as early as possible to get a higher price, as in most other vegetable crops. 2. Control transmission media: Aphid can be used 40% Dimethoate Emulsion 2000 Dilution or 25% Siphosulfate 1000 Dilution, or 50% Diluted Mist 3000 Dilution, or 21% Green Pest 1500-2500 Dilution Solution, or 1% gram 500-fold dilution, or 10% imidacloprid wettable powder control.
Second, the main insect pests
The main insect pests of the root mustard were cabbage caterpillars, diamondback moths and aphids. The leaves of the plant were damaged by leafflies.
1, cabbage caterpillar
The adult is called cabbage butterfly. It occurs throughout the country. The larvae feed on the leaves, perforating the leaves, and nicking. The adult stage may also be compromised. However, no matter what period, the degree of damage was not as serious as that of cabbage and Chinese cabbage. The green larvae of cabbage caterpillars are densely covered with fine hairs and black spots.
Control methods: timely removal of stubble leaves and weeds in the field. When the temperature is above 20°C, it can be controlled by 500-800 times of Bt emulsion or bacillus or 7216 spray. This is needed for the production of pollution-free vegetables and it should be advocated as much as possible with the use of such agents. Use 2000 dilution of 50% phoxim EC or 500 times dilution of 25% insecticide, or 3000 times dilution of 25% deltamethrin, or 5% of cadmium, 5% of tetracycline Liquid or efford 1500-fold dilution, or Cainong 5 1000-fold dilution, or NET Yee-bao 1500-fold dilution, or pest control 1,000 times dilution.
2. Plutella xylostella
Plutella xylostella is also called hanging filarial, two tips. Larvae damage leaves, tender stems and young fruit. The instar worms eat leafy meat and have a residual epidermis. After 3rd age, the leaves were eaten as holes, and when severe, the leaves were meshed or only leaves were left.
The larvae are pale, light green, spindle-shaped, and sparsely long black bristles on the body. Immediately after being frightened, he twisted his body and retreated or drooped. The hanging threadworms got their name. Suddenly, after the grief ceased, it continued to cause harm. The most serious damage is from August to October every year.
Control methods: Rotate with non-cruciferous crops; timely remove stubble leaves and weeds in the field, and between summer and autumn, pay attention to “broken bridgeâ€. Use 400 ml of Bt emulsion per acre vegetable field. It can be controlled by 3,000-fold dilution of thiotetracycline 3,000-fold dilution; or 5% rigorous ginsenoside suspension 4,000-fold dilution, or 98% Bataan soluble powder 200-fold dilution, or 5% karate emulsifiable concentrate 3000-fold dilution. Different types of medicaments are used interchangeably to avoid giving the diamondback moth resistance.
3, locusts
Locusts are not only the media that spread the virus, but also cause harm to the plants themselves. The larvae are small in size, with wings and boring fleas. The winged pheasant has a well-developed thorax, two pairs of transparent membranous wings, a large fore wing, and a small hind wing; a wingless worm, the body is mostly ovoid, and its body color is yellow, green, brown and dark brown. Some ticks can secrete membranous, waxy, and waxy silks. Both winged and wingless cockroaches have a nearly conical tail piece at the end of their abdomen.
The locusts have two peaks in the year: from the middle of April to the beginning of June, the amount of maggots increased and formed the first peak. It was only during this period that the strains of the root mustard were in the field and that the production-grown root mustard had not been in the field and had been harvested in the previous year. Therefore, this peak will not cause harm to the seedlings. The second peak is autumn and winter. The adults and nymphs cluster on the young leaves to sap, often causing the leaves to lose their green, yellow, wilting and shrinking.
Capillary Microcirculation Microscope
Micirculation Microscope:
The Nailfold Capillaroscopy Microcirculation Microscope is an advance medical photoelectric apparatus,equipped with built in special LED light source,used mainly in observation on human nail fold capillary microcirculation or term as video Nailfold capillaroscopy,Such as capillary blood flow, abnormal microcirculation of the vascular structure, cell adhesion, through its powerful optical magnification. Undistorted, real time dynamic video streaming via Sony CCD imaging device onto the LCD monitor screen.
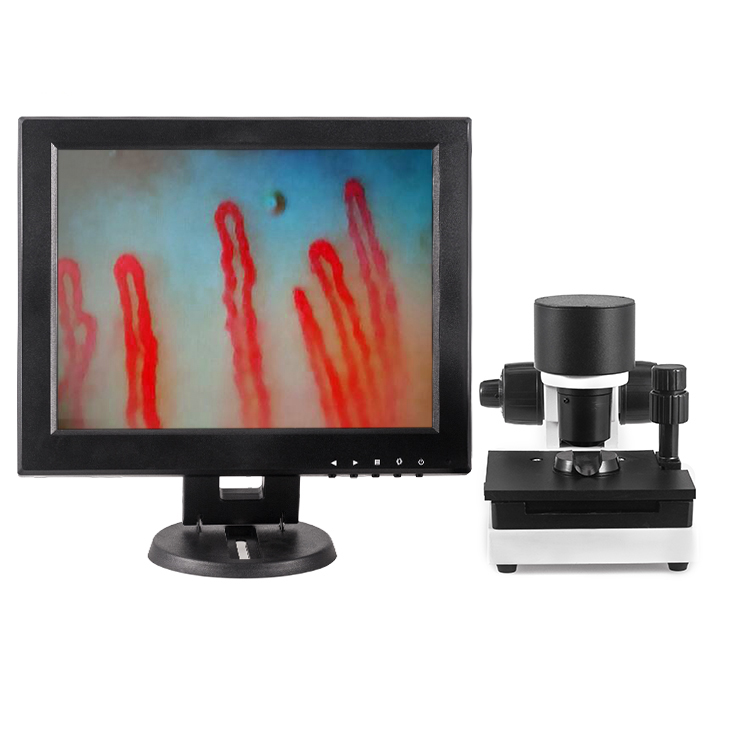
Digital Microscope,Micirculation Microscope,Blood Microcirculation Microscope,Microcirculation Microscope Device
Shenzhen Guangyang Zhongkang Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.szlighttherapymachine.com