Tulip planting techniques
To grow the tulips, choose empty, sunny, well-drained, loose and fertile, and plant the groundwater table at a low level. The soil pH should be 6.5-7.
Before planting, fully deepen the soil by 20-25 cm and apply a decomposed organic fertilizer as base fertilizer, such as cow dung, rot leaf or compost soil. In order to develop the bulbs better, the flowers are more colorful and some superphosphate is applied.
Tulips are planted in mid-November in the fall. The depth of planting is consistent with the depth, which is generally about twice as high as the bulb height. The plant spacing is 8-10 cm and the row spacing is 12-15 cm.
When planting, the soil should be slightly moist and should not be too dry or too wet. Grasping soil with hands and loosening the soil mass is loose. After planting, cover with fine soil, fill with clear water (if rain is needed after planting, do not need watering), and cover with a layer of straw to prevent the soil from being arid.
In mid-February of the following year, fresh shoots were applied once before emergence and before the buds in early March. During the growth period, it is generally not necessary to water the soil to keep the soil moist. In case of drought, it is also necessary to pay attention to adequate irrigation with fresh water. If there is too much rain, it should be drained in time.
In addition to viewing, if used to preserve varieties and produce bulbs, they should be removed in time when the buds are seen, reduce nutrient consumption and promote bulb growth.
After the last part of the local branches withered, that is, from late 5 to mid-June, the bulbs should be dug to dry, clean the ball, sorted and packed in bags, placed in a ventilated, dry place. If the temperature is too high, poor ventilation will affect the differentiation of flower buds and even cause degradation of the bulbs. Therefore, it is advisable to store them in cold storage in high-temperature areas in summer.
Tulips are prone to epidemics, spring rains, severe weather damage, and disease on leaves, flowers, petals, and bulbs. In the early stages of the disease, the lesions were thin and brown, and the petals were constantly infested. The petal was pale to pale yellow. When the lesions were enlarged seriously, the leaves were rotted and withered. The bulbous and cortical surfaces were dark brown and corrupt. Prevention methods are: When planting bulbs, they should be carefully selected, and the sick bulbs should be removed. Before planting, bulbs should be disinfected and soaked with carbendazim or thiophanate-methyl 200-500 times for 30 minutes. From the middle of March to the flowering stage, carbendazim or thiophanate-methyl 1000 times can be sprayed once every 10 days.
Double Packed Yellow Waxy Corn Cob
The most common waxy and sweet corn market, waxy corn nutrient content is higher than ordinary corn, contains 70-75% starch (and almost all amylose), more than 10% protein, 4-5% fat and 2% multivitamin, has more grain, VA, VB1, VB2 than rice protein, fat and VB2 highest content. Yellow corn also contains carotenoids like rice and wheat. The molecular weight of glutinous corn starch is more than 10 times smaller than that of ordinary corn. The starch makes glutinous rice sticky and soft, which is softer than that of ordinary hard corn. It has more than 20 percent more digestibility than regular corn and is suitable for people with irregular teeth. At the same time, the amylose (a polysaccharide) content is very high, not suitable for diabetics.
Waxy corn is also called sticky corn. The grain has a coarse, waxy endosperm that resembles a glossy, transparent grain, such as a hard, dented corn. Its chemical and physical properties are controlled by a recessive gene located on chromosome 9. 100% of the starch in the endosperm is amylose.
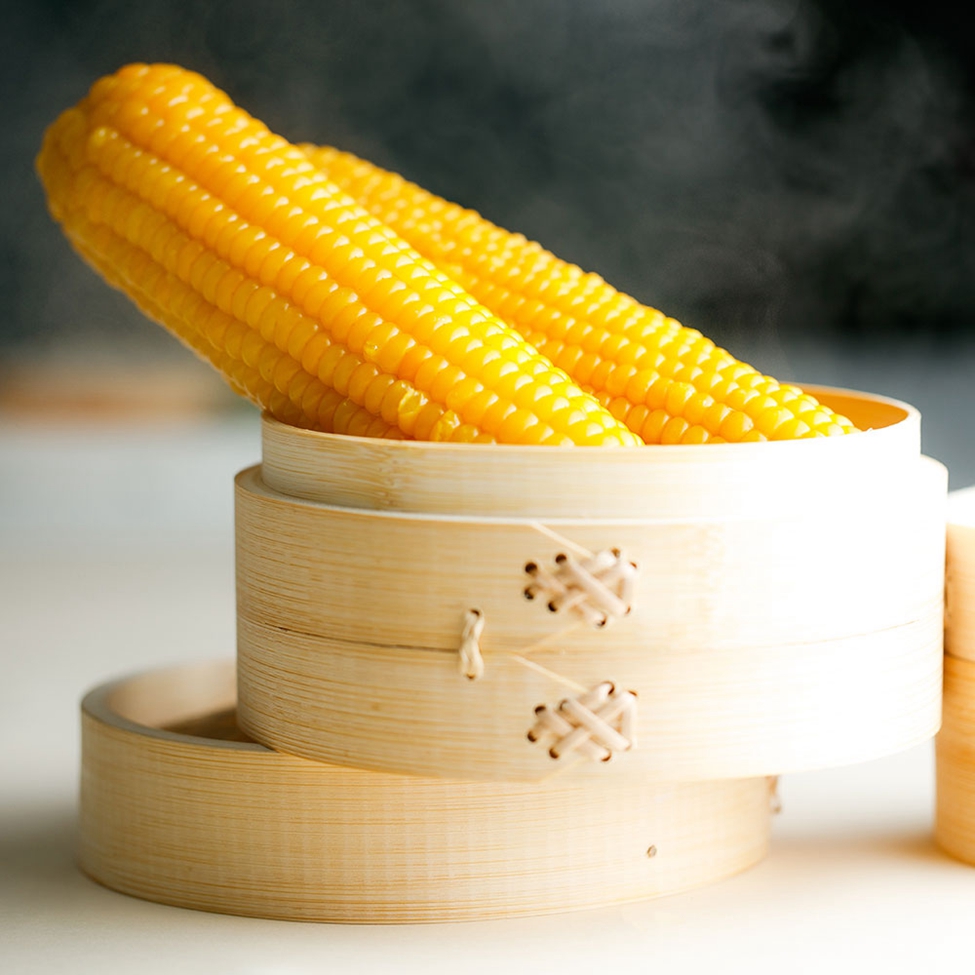
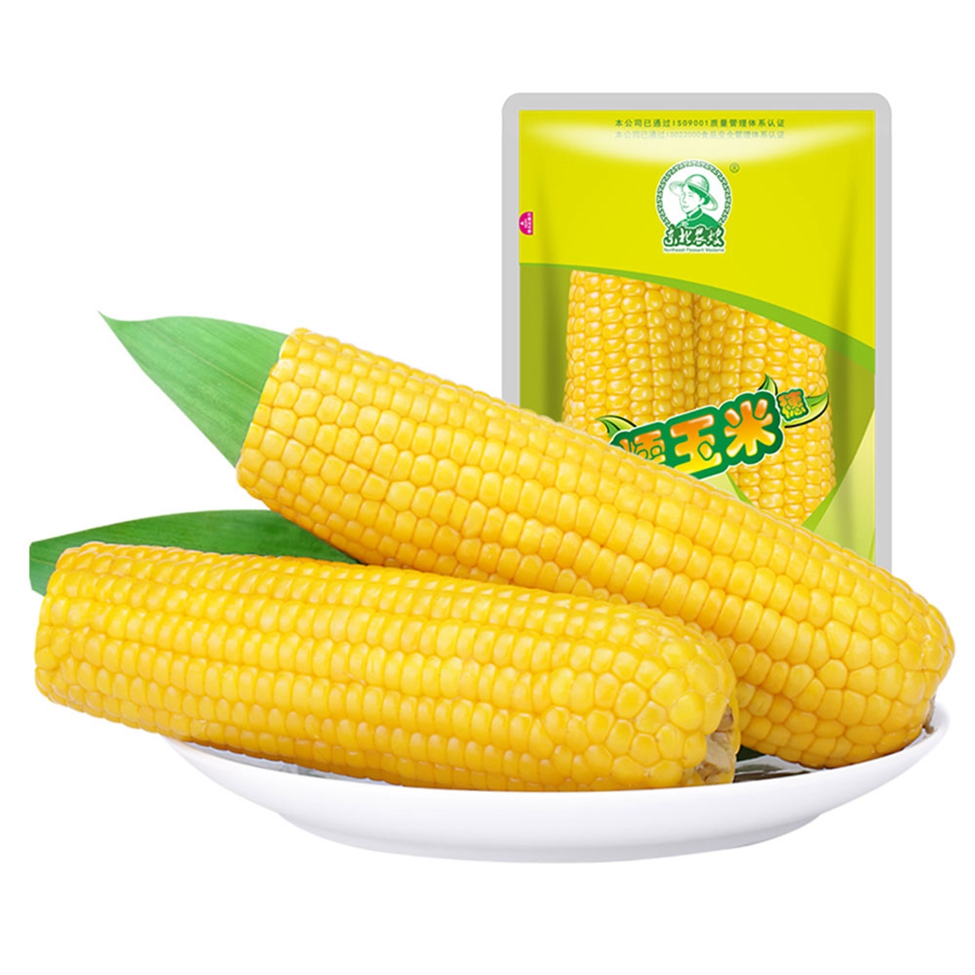


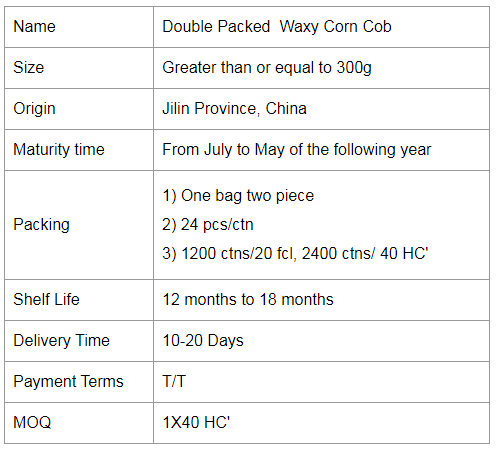
Glutinous Corn,Yellow Corn Cob,Corn On The Cob,Double Packed Yellow Waxy Corn Cob
Jilin Province Argricultural Sister-in-law Food Co., Ltd. , https://www.nongsaocorn.com