Among the 135 hospitals, who is the most comprehensive hospital with comprehensive strength in China?
Recently, in order to promote the sharing of medical and health information, according to the requirements of the “13th Five-Year National Population Health Information Development Planâ€, the National Health Statistics Information Center organized the 2017 National Health Information Interconnection Standardization Maturity Assessment Work. The technical evaluation of the relevant regional and hospital informatization construction levels was voluntarily applied for, and the results of the evaluation of 15 regions and 50 hospitals participating in the assessment were publicized.
According to the publicity situation, a total of 50 hospitals have received corresponding interconnection ratings. Prior to this assessment, the National Health Information Interconnection Standardization Maturity Assessment has been carried out in four phases. Up to now, a total of 90 hospitals have received corresponding ratings, as shown below:
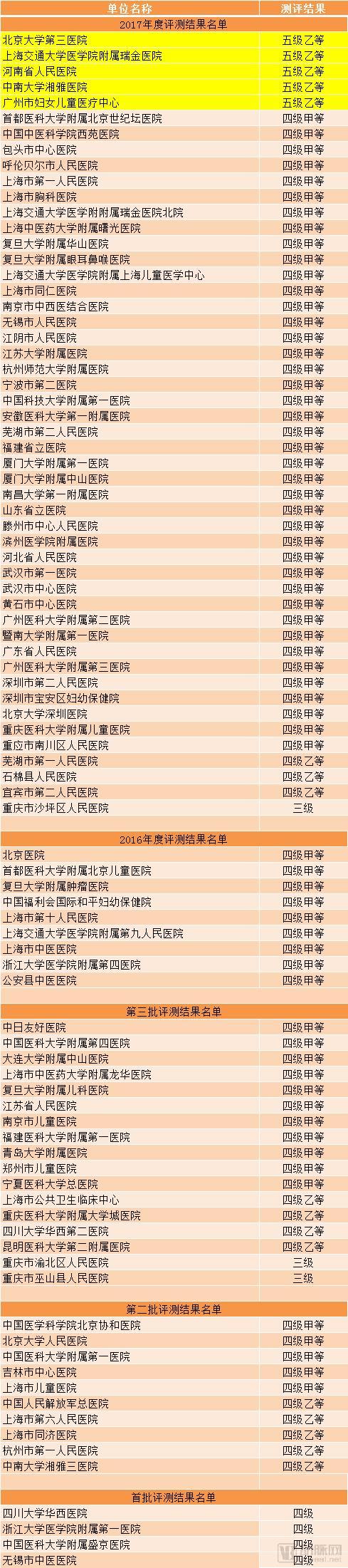
Among the participating hospitals, Peking University Third Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine Ruijin Hospital, Henan Provincial People's Hospital, Central South University Xiangya Hospital, Guangzhou Women and Children Medical Center became the first hospital to receive the five-level evaluation of interconnection. .
Compared with previous years, the number of hospitals participating in the evaluation in 2017 is the highest in history, which also reflects the fact that the level of informatization and interconnection of domestic hospitals is increasing year by year.
In order to further analyze the comprehensive strength of domestic hospital informationization and interconnection, the arterial network (public number: vcbeat) combines the high level of the “Evaluation Standards for Application Level of Electronic Medical Record System†of the current National Health and Family Planning Commission Hospital Management Research Institute. The list of hospitals, as well as the HIMSSEM RAM rating results, and based on the sum of the total scores, according to the corresponding standards, calculated the current 135 hospitals with the highest comprehensive strength in China.
The arterial network is statistically based on the data. The results and criteria are as follows:
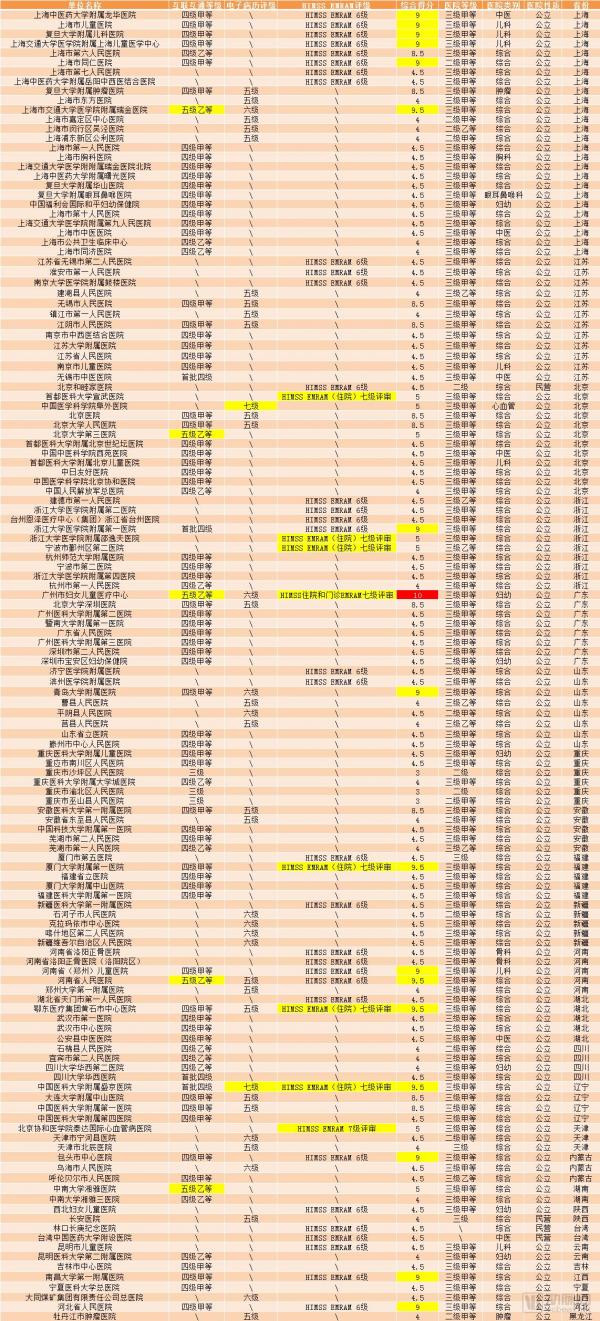
This score is the final score based on the sum of the interoperability level and the higher of the other two ratings. Among them, the interoperability level is counted as 3 points, the fourth level is counted as 4 points, the first batch of 4th and 4th grades is counted as 4.5 points, and the fifth grade is counted as 5 points, and the electronic medical record system function application level is calculated. Levels 5, 6 and 7 are 4 points, 4.5 points and 5 points respectively. Levels 6 and 7 of HIMSS EMRAM are counted as 4.5 and 5 points respectively. Since the latter two ratings have a high degree of overlap, the units that both pass are scored on a higher basis.
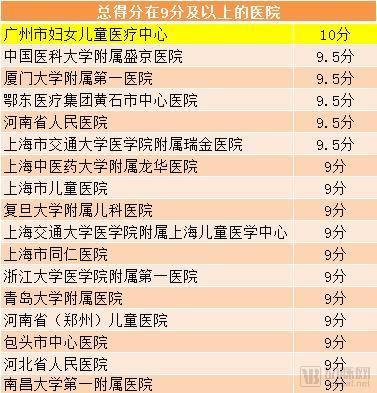
According to the scoring standard, the following 17 hospitals have become the units with the highest scores and the strongest comprehensive strength. Among them, the Guangzhou Women and Children Medical Center successfully climbed to the top with a unique score of 10 points.
It can be seen from the comprehensive score and quantity that nearly half of the 135 hospitals scored 4.5 points. Objectively, they only participated in the intercommunication assessment, but did not participate in the other two grades, so the score was slightly deficient, but this result does not mean that these hospitals have no ability to obtain other grades.
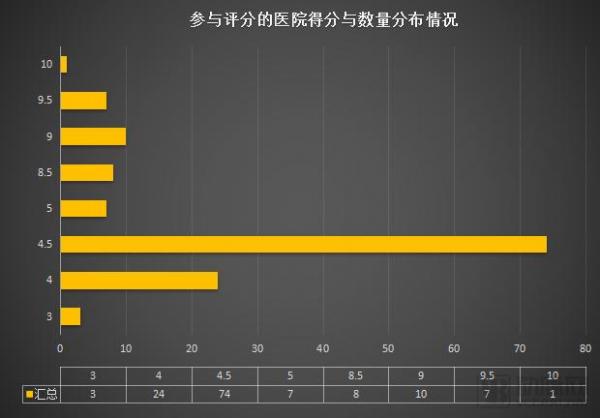
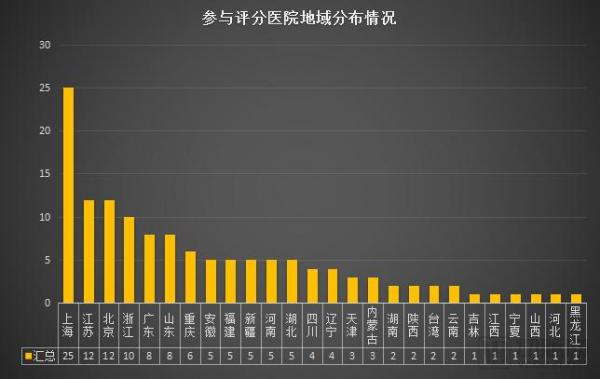
Geographically, Shanghai hospitals have become a concentrated implementation area for interconnection. In addition, the interconnection between Jiangsu and Zhejiang provinces and hospitals in Beijing is in the second echelon, and the potential of other cities has yet to be tapped.
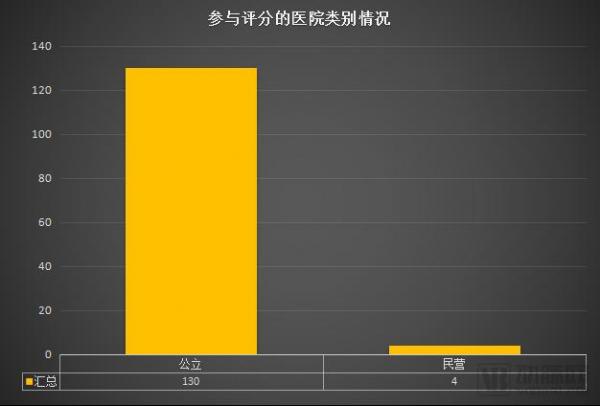
Among the hospitals that were short-listed, 130 were public hospitals. Apart from the two in the Taiwanese area, only two private hospitals, Beijing Hejia Hospital and Chang'an Hospital, were selected and scored below 5 points. This shows that there is still a large room for improvement in the level of interconnection and informatization of domestic private hospitals.
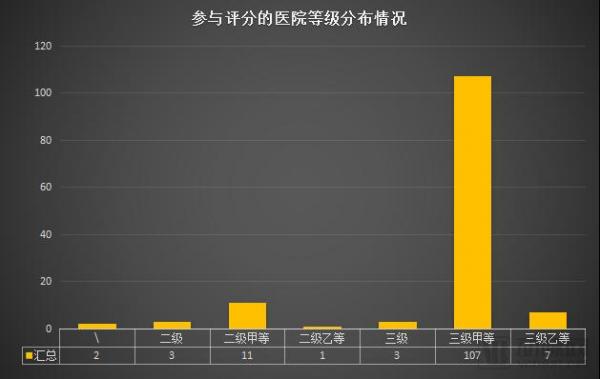
In terms of grades, most of the hospitals that have been short-listed are top-three hospitals, and other grades of hospitals are less, and the room for improvement is still relatively large.
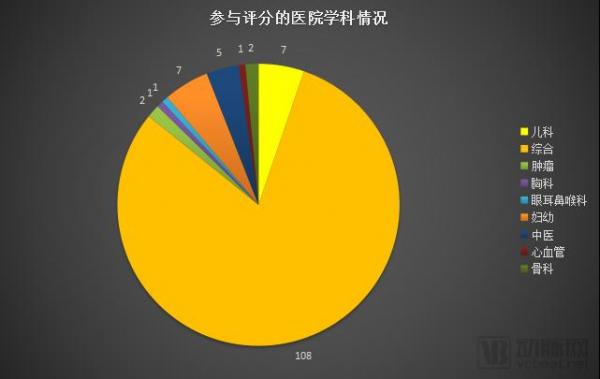
In this short-listed hospital, in addition to general hospitals, the arterial network found three key potential specialist hospitals: Pediatric Hospital, Maternal and Child Hospital and Chinese Medicine Hospital . It can be seen that the requirements for interconnection and interconnection of these three types of hospitals are currently the most demanding specialized hospitals in China.
Evolution of connectivity, new trends in the future
On April 28, the General Office of the State Council issued the "Opinions on Promoting the Development of "Internet + Medical Health"" (hereinafter referred to as "Opinions").
Its purpose is to promote the implementation of the Healthy China strategy, improve the modernization of medical and health management, optimize resource allocation, innovate service models, improve service efficiency, reduce service costs, and meet the growing health and health needs of the people.
The "Opinions" clearly stated that all regions and relevant departments should coordinate and promote the construction of a unified national authority, interconnected and universal health information platform, and gradually realize the interconnection and communication with the national data sharing and exchange platform.
More than two levels of hospitals should improve the function of hospital information platform, integrate various system resources in the hospital, and improve hospital management efficiency. Third-level hospitals must realize the sharing of hospital medical service information by 2020, and conditional hospitals should be realized as soon as possible.
This signal released by the State Council will further accelerate the pace of interconnection between hospitals at all levels.
In the development process of hospital interconnection in recent years, it has also undergone some changes in content. Take the electronic medical record rating as an example.
On March 23, 2018, the Hangzhou International Expo Center held the China Hospital Information Network Conference (2018CHINC).
"Digitalization, informationization, Internetization, and intelligence" have become the main tone of the conference. On this day, the electronic medical record rating evaluation ushered in new standards. On the basis of the highest level of 7 in the past, it has added a more difficult level 8.
Experts at the meeting analyzed the five major imperfections of the 2011 version of the application level quantitative scoring method, including:
1. There are many low-grade hospitals in China's electronic medical records, and it is necessary to increase the degree of discrimination in the assessment;
2. The scope of evaluating electronic medical records is not completely covered. There is a new demand for medical quality control, knowledge base application, and data application, which is the current direction for guiding applications;
3. Some parts of the current standard evaluation project overlap;
4. Some project descriptions are not clear enough to affect the understanding of use;
5, some hospitals blindly pursue high levels, resulting in low actual data quality .
Therefore, in response to these five imperfections, this electronic medical record grading evaluation has been revised around six basic principles:
1. Maintain stability: make the previous evaluations comparable as much as possible;
2. Increase the degree of discrimination: add a level and adjust the level , and move some functions into the requirements of 1-2 levels;
3. Increase the scope of assessment: the content of medical quality improvement is included in the evaluation, and the application role is increased;
4. Concretize the contents of inspection, inspection and treatment items in the original evaluation function;
5. Add a survey dimension and incorporate data quality (information quality) into the assessment . List the assessment requirements for data quality for different levels;
6. Revise the contents of the original instructions to avoid content that is ambiguous.
The most important point is that data quality has become the focus of rating , which eliminates the possibility of past hospitals using fake data to pass the review, and also makes the review more return to the essence, that is, the accumulation, sharing and utilization of truly valuable big data.
In addition to changes in the electronic medical record rating, the standardization of maturity of interconnection and intercommunication in the past two years is also in the process of continuous pilot improvement.
In September 2017, the National Health and Family Planning Commission's Statistical Information Center officially issued an updated version of the National Medical Health Information Area (Hospital) on the basis of the “Policy Information Interconnection Standardization Maturity Assessment Program (Trial)†document published in 2015. Information Interconnection Standardization Maturity Assessment Program (2017 Edition).
The following figures are for the 2015 and 2017 editions:


The difference between the two versions of 2015 and 2017 is mainly in the definition and scope of the content of the test.
In 2015, the standardization of hospital information interconnection standardization was mainly divided into two parts: product testing and project application evaluation. The two include four parts : data resource standardization construction, interconnection and standardization construction, infrastructure construction, and interconnection and application effects .
In contrast, the 2017 version of the assessment description is adjusted for both laboratory testing and project application evaluation . The evaluation of the standard conformity test and the evaluation of the actual application effect of the interconnection are carried out for the medical institution informationization project with the electronic medical record and the hospital information platform as the core.
Compared with the old version, this definition highlights the differences between actual and standard test. For the weight of the practical application of hospital interconnection, it has a strong promotion effect.
Although it seems that the two versions have little difference in the test content, the 2017 version follows a wider range of standards and documents, such as the 2017 version of the shared document standard compliance test mentioned, according to WS/T 500- 2016, WS/T 483.2 -2016 and other standards require quantitative testing of the structure and content of the normative, which is quite different from the 2015 version. This also means that the 2017 version has a certain degree of improvement in the quality and extent of shared data in hospitals.
Although the two versions differ in definition and scope, the first, second, third, fourth, fourth, fourth, fifth, and fifth grades remain unchanged:
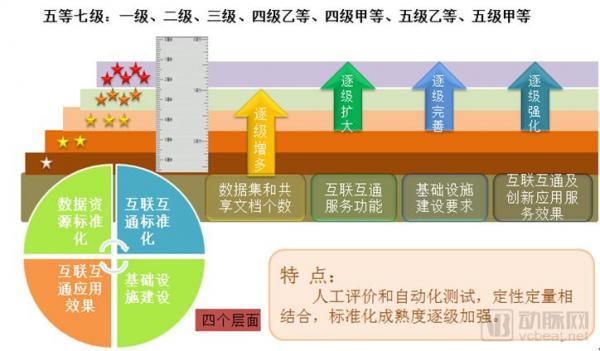
Industry development trend analysis
The comprehensive maturity assessment of information exchange and the evaluation of electronic medical record grading evaluation in comprehensive hospitals can be found that the quality and sharing level of medical data will become the top priority of hospital informationization construction at all levels in China.
Combined with the current status of interconnection and intercommunication of domestic hospitals, the arterial network judges that for information enterprises to find industrial increments, they can focus on finding breakthroughs in these directions:
1. Private hospitals of Grade II and above;
2. Pediatric hospitals, maternal and child hospitals and Chinese medicine hospitals;
3. Chongqing, Sichuan, Anhui, Xinjiang, Hubei and other provinces and cities.
Shower Gel,Shower Cream,Body Shower Gel,Foaming Shower Gel
Guangzhou Lingxue Cosmetics Co., Ltd , https://www.gzlxgj188.com