A major breakthrough! Zhang Feng Nature issued a message: CRISPR can start any gene
MIT scientists have reworked the most popular gene editing system, CRISPR/Cas9, which was published in the December 10 issue of Nature. Now, people can use this technique to effectively activate any gene in living cells.
This system allows scientists to more easily study the functions of different genes, said Feng Zhang, a pioneer in CRISPR technology who led the research.
The modified CRISPR technology allows rapid screening of the entire genome for help in identifying genes involved in specific diseases. In this study, Zhang Feng et al identified several genes that make melanoma cells resistant to cancer drugs.
New features of CRISPR
CRISPR was originally an immune system against bacteria infection. Previously, this system was used to create a gene editing complex that includes the Cas9 enzyme and the guide RNA. Guide RNA to a specific sequence in the genome, telling Cas9 where to cut.
In the past two years, Cas9 tools have been widely used to shut down or replace genes, and Zhang Feng and others have successfully modified it to start genes.
Some people have tried to start the gene with the CRISPR system. They inactivated the splicing activity of Cas9 and linked Cas9 to the activation domain, which recruits transcriptional machinery and initiates the transcription process. However, these efforts do not consistently initiate gene transcription.
Zhang Feng et al. previously obtained the structure of Cas9 binding to guide RNA and target DNA, and they decided to modify CRISPR-Cas9 on this basis. "Having known its 3D form, we can improve this system reasonably," Zhang Feng said.
In the past, the activation domain was attached to the end of Cas9, but the effect was not satisfactory. The MIT team realized that the two small loops that RNA protrudes from the Cas9 complex are better junction sites, so the activation domain is more flexible when recruiting transcription machines. They successfully activated ten genes with the modified CRISPR system. The transcription of these genes has more than doubled, and the activity of many genes has even increased by several orders of magnitude.
Whole genome transcriptional activation
Subsequently, the researchers established a library of 70,290 guide RNAs to target more than 20,000 genes in the human genome. They thus identified the gene that makes melanoma resistant to the drug PLX-4720. PLX-4720 is more effective in patients with BRAF mutations, and the remaining cancer cells will grow into new tumors, leading to cancer recurrence.
The researchers introduced the CRISPR element into a large number of melanoma cells cultured in vitro, and the different cells correspond to the guide RNA of different genes of the target. They then treated the cells with PLX-4720 to identify genes that help cancer cells survive. In fact, they did find several new resistance genes. Such research can help people develop new cancer drugs and prevent tumors from gaining resistance.
Next, Zhang Feng's lab plans to continue screening for genes that activate autism or neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's.
Source: Biopass
Steroid hormones, also known as steroid hormones, are a class of tetracyclic aliphatic hydrocarbon compounds with a cyclopentane polyhydrophenanthrene nucleus. It has very important medical value. It has a clear role in maintaining life, regulating sexual function, body development, immune regulation, skin disease treatment and birth control.
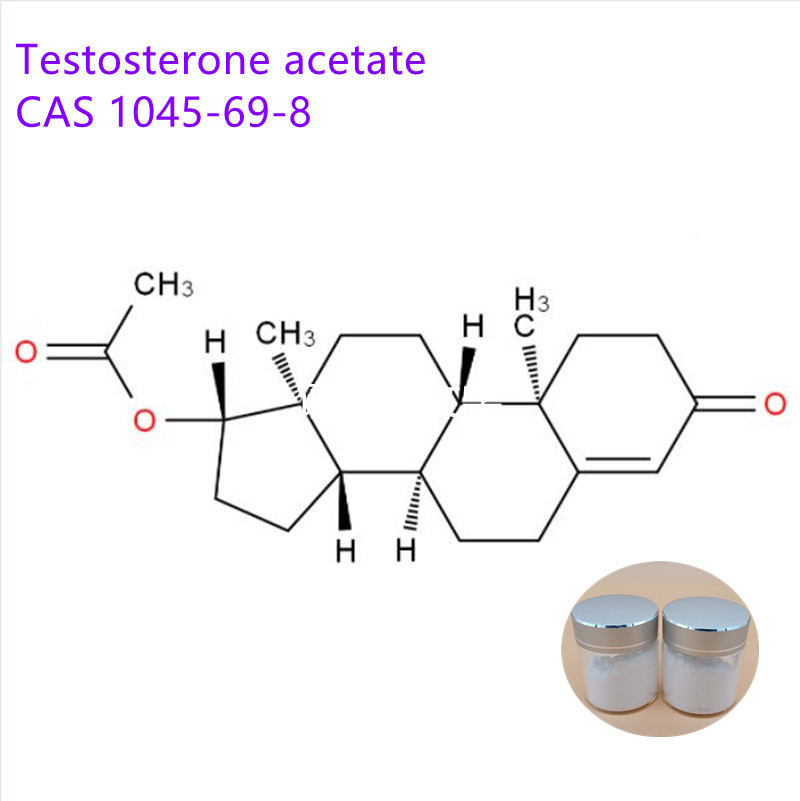
Steroids include steroids (eg cholesterol, lanosterol, sitosterol, stigmasterol, ergosterol), bile acids and bile alcohols, steroid hormones (eg adrenal corticosteroids, androgens, estrogens),

Our company specializes in providing steroid series products, welcome to inquire and order

Steroids Oil,Steroid Powder,Steroids Injections,Steroid Powder And Oil
XI AN RHINE BIOLOGICAL TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD , https://www.xianrhinebiotech.com