Do you understand how many prescriptions are used? --Talk about pharmacokinetics PK
When talking about medication instructions, such as Xiaobian, the layman can see that the knowledge involved is unfathomable. Think about a new drug, from the previous non-clinical exploration experiments, and finally get clinical validation to the market, the experience is not a cold day.
Well, such a long-term research is mainly about faltering. Keke... This is not a matter of one or two sentences. It’s clear that it’s clear...
but! For pharmacokinetics (PK) and pharmacodynamics (PD), it can be said that the key research content, the two complement each other, are indispensable.
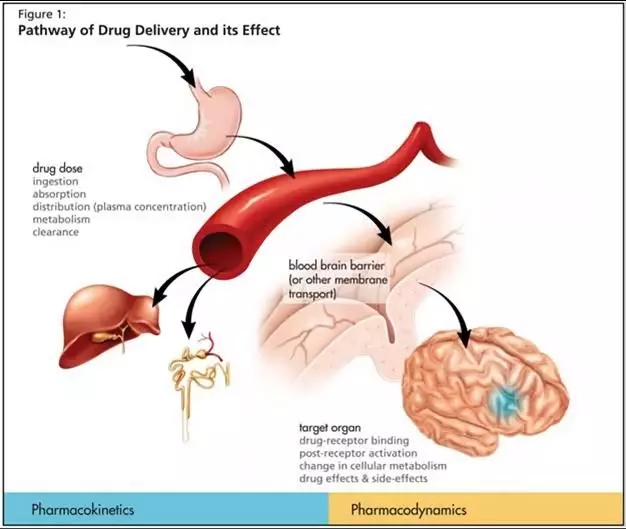
Image from the network [1]
Today, Xiaobian will start with everyone from the non-clinical PK.
PK is a quantitative study of the changes in the in vivo processes of absorption (A), distribution (D), metabolism (Metabolism, M) and excretion (E).
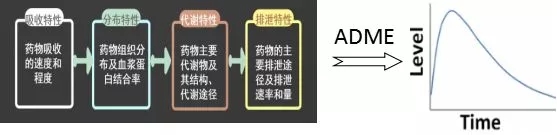
absorb
Definition: The process by which a drug is transported from the site of administration into the blood
The site of administration is usually divided into intravascular and extravascular administration. Intravascular administration generally refers to direct entry into the blood through veins or arteries (no absorption process); extravascular administration includes oral, muscle, skin, etc. (into the blood must be absorbed) Process), the drug loss caused by the drug for the first time through the metabolic organs (such as the gastrointestinal wall and liver) is called the first-past effect .
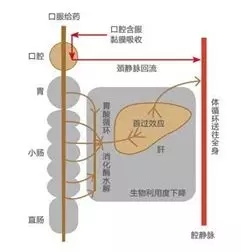
First pass effect [2]
Evaluation of quality of drug absorption is the bioavailability (bioavailability, BA), i.e. the relative amount of the blood circulation reaches the site of administration

Image from the network [3]
For example, if 1g is administered and 0.5g of drug enters the blood circulation, then we say that the BA of this drug is 50%. (This concept is very important, please keep in mind, keep in mind!)
There are many factors affecting the absorption of drugs, such as: the route and location of the drug (such as intravenous injection, intramuscular injection - remember the ass needle when you are a child? Oral - most popular, safe, convenient, economic, and many advantages); physical properties of the drug (such as acid and alkali, solubility, etc.) and dosage form factors, physiological factors and pathological factors .

Image from the network [4]
For protein macromolecules such as antibodies, the BA value after oral administration is extremely low , mainly because 1 protein is easily denatured in acidic gastric juice; 2 protein is easily degraded by a large number of hydrolases in the gastrointestinal tract; 3 protein is bulky It is highly polar and is not easily absorbed by gastrointestinal epithelial cells by diffusion [5] .
Therefore, most of the monoclonal antibodies are administered intravenously (IV), and a small number are administered subcutaneously (SC) or intramuscularly (IM) . Subcutaneous or intramuscular injections mainly enter the body through the lymphatic circulation rather than the capillaries. System, slow absorption, peak time delay [6] .
distributed
Definition: The process by which a drug is distributed along the blood to various tissues of the body.
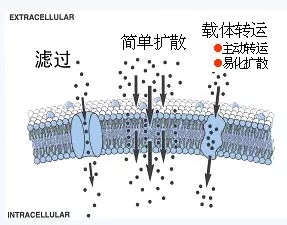
The way drugs pass through the cell membrane [7]
The rate and extent of its distribution are mainly related to tissue blood flow rate, physiological barrier (blood-brain barrier, placental barrier, etc.), drug-tissue affinity, drug plasma protein binding rate, drug fat solubility and other factors.
The indicator for measuring the broad distribution of drugs is the apparent volume of distribution (Vd), that is, when the drug absorption reaches equilibrium or steady state, the total amount of drug in the body (A) is theoretically occupied according to the blood concentration (C). Volume volume, namely: Vd (L) = A (mg) / C (mg / L), the greater the Vd value, indicating that the drug is widely distributed in the body, and vice versa, the drug distribution limit, tissue intake rate is low [8] .
For drugs, it is generally considered that the free form of the drug in the body is important for its efficacy. However, free macromolecular drugs may be the main source of immunogenicity, especially macromolecular drugs often do not bind to plasma proteins . The size of the molecular weight limits the biological product to plasma (lymph) and interstitial spaces, but is capable of binding to the target with high affinity, which leads to an increase in the volume of the distribution and the interaction between the biological product and their target may affect Vd value.
metabolism
The drug is often converted into a form that is easy to excrete before excretion, such as decreased fat solubility, increased polarity, etc., and is called metabolism of the drug. Drug metabolism is essentially an enzymatic reaction . For example, in the drug metabolism enzymes in the liver, cytochrome P450 oxidase (CYP enzyme) plays an important role. The size of the drug enzyme activity directly determines the intensity of the drug action.
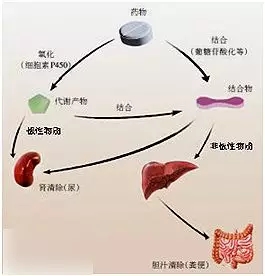
Image from the network [9]
Macromolecular drugs are usually not metabolized by CYP enzymes, mainly in the kidneys (lower molecular weight biological products) and the liver is catabolized by proteolytic enzymes . Its drug metabolism elimination pathway mainly includes glomerular filtration, enzymatic hydrolysis, receptor-mediated endocytosis elimination and anti-drug antibody (ADA)-mediated elimination .
excretion
The process of absorbing the drug or the metabolized product that has entered the body into the body. The main route of excretion is renal urinary excretion, bile excretion, and excretion of feces (intestines).
Macromolecular drugs are mainly excreted through the kidneys. Since macromolecular drugs are biologically active, their toxic effects are often related to drug efficacy, and the main toxic effects are kidney toxicity and hepatotoxicity . It is currently believed that the renal toxicity of macromolecular drugs is mainly due to the difficulty of renal excretion caused by large molecular weight, which may cause inflammatory reactions [6]. On the other hand, some antibody drugs may also cause cytokine storms, causing serious damage to the body.
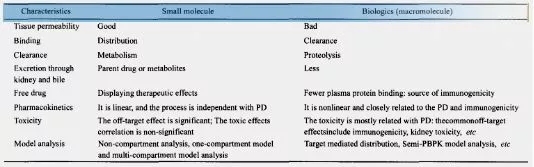
Table 1 Comparison of ADMET(absorption,distribution,metabolism excretion and toxicity)characteristics between macromolecules and small molecules [6]
Significance of nonclinical pharmacokinetic research
For the significance of the research of non-clinical pk, I believe that you don’t have to edit a little bit to say that everyone’s heart is clear.
The most important, of course, is to provide an important basis for the design and optimization of clinical research drug delivery programs , to ensure the safety and rationality of clinical research drugs, and to help understand the efficacy or toxicity of target organs, to clarify the efficacy Or the material basis of toxicity, also provides important clues for pharmacodynamics and toxicological evaluation , and has guiding significance for the development of safer and more effective new drugs and the formulation of poisoning and rescue measures [10] .
Reference material
[1]http://#i=0&pn=30&sn=0&id=9d324f0ca8d8229b06a36c6af915e825
[2]https://baike.so.com/doc/5327951-5563123.html
[3] https://?id=666047949
[4] http://kengdie.com/60059/
[5] Guo Jianjun et al. Progress in pharmacokinetics of monoclonal antibody drugs, Chinese Pharmacological Bulletin 2016 Feb; 32(2): 172-6
[6] Zhang Cuifeng et al. The absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion and toxicity characteristics of macromolecular drugs and the application of pharmacokinetic models, Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2016, 51(8): 1202 — 1208
[7]https://
[8] Su Lequn editor, pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetic interpretation, clinical pharmacy series of books.
[9]https://baike.baidu.com/pic/%E8%8D%AF%E7%89%A9%E4%BB%A3%E8%B0%A2/220351
/0/5243fbf2b211931354deb01d62380cd790238dfafr=lemma&ct=single#aid=0&pic=5243
Fbf2b211931354deb01d62380cd790238dfa
[10]http://mooc1.chaoxing.com/course/98206619.html

Scan code to pay attention to the 100 Olympics map to learn more about consulting
Molecular Diagnostic PCR Reagent for Pathogens
PCR,Molecular diagnostic ,PCR Reagent,,Respiratory Infections,Gastrointestinal Infection,STD Infection,Vetor-borne Diseases
Shenzhen Uni-medica Technology Co.,Ltd , http://www.unimedicadevice.com