Talking about filter selection and misunderstanding
introduction
As the main component of pollution control of hydraulic system, hydraulic filter is reasonable in design and selection. Whether the daily use (maintenance) is correct is directly related to the safety and reliability of the system. In practical applications, many users still have many misunderstandings on the selection and use of filters. Failure to correct them will affect the normal and reliable operation of the hydraulic system.
1 Filter selection error in hydraulic system
1.1 Misunderstanding 1: Selecting a high-precision oil absorption filter can not only effectively protect the pump, but also ensure the cleanliness of the system. The particle contamination in the oil will aggravate the wear of the pump and affect the service performance and life of the pump. Contaminants may also jam the pump, seriously affecting the safety and reliability of the system. Therefore, some users have chosen a high-precision oil suction filter, which is considered to protect the pump and ensure the cleanliness of the system. However, the high-precision oil suction filter is easy to block due to excessive contaminants, resulting in poor pumping of the pump, which leads to suction and accelerates the wear of the pump, which seriously affects the safety of the system. Therefore, the pressure drop of the suction filter is strictly controlled. General hydraulic systems may consider installing a low-precision suction filter to protect the pump and installing a filter in front of the contaminant-sensitive components to control the effects of particle contamination. In order to most effectively intercept the contamination of the circuit due to component wear or external intrusion, it is recommended to install a return filter to control the cleanliness of the entire system. At the same time, the pipeline and fuel tank should be thoroughly cleaned before the system is operated to ensure the degree of oil contamination. In this way, the degree of oil contamination of the entire system is basically controlled, protecting both the pump and the entire system.
1.2 Misunderstanding 2: The rated (nominal) flow of the filter is the actual flow of the system.
The nominal flow rate of the filter is the flow rate through which the oil filter is cleaned at a specified viscosity while the oil viscosity is 32 cst. However, in practical applications, the viscosity of the oil changes at any time due to the difference in the medium used and the temperature of the system. If the filter is selected according to the rated flow rate and the actual flow rate of 1:1, the resistance of the oil passing through the filter will increase when the viscosity of the system oil is slightly larger (for example, the viscosity of the 32nd hydraulic oil at 0 °C is about 420 cst), even The contamination of the filter is blocked and the transmitter sends a signal, and the filter element is considered to be clogged. Secondly, the filter element of the filter is a consumable part, and it is gradually polluted during work. The actual effective filtration area of ​​the filter material is continuously reduced, and the resistance of the oil passing through the filter quickly reaches the polluting signal sent by the transmitter. In this way, the filter needs to be cleaned or replaced frequently, which increases the user's use cost.
At present, all domestic filter manufacturers have specified the rated flow rate of the filters they produce. Based on past experience and many customers' usage, when the system uses oil as general hydraulic oil, it is recommended that the filter be selected according to the following flow rate. Multiple selection: 1 The rated flow of the oil absorption and return filter is more than 3 times of the actual flow of the system; 2 The rated flow of the line filter is more than 2.5 times the actual flow of the system. If you use oil other than general hydraulic oil or high viscosity hydraulic oil, please consult the manufacturer's selection.
1.3 Misunderstanding 3: The higher the accuracy of the filter selection, the better.
Solid contamination in hydraulic systems is the main cause of hydraulic system failure, so high-precision filters are used to control pollution. In fact, this will not only increase the manufacturing cost of the system, but also shorten the service life of the filter. So how to choose the accuracy of the filter reasonably? It is mainly determined by the contamination requirements of the components of the hydraulic system. The higher the cleanliness required by the components, the higher the accuracy of the filter selection. When the wear particles enter the motion gap of the component, a chain reaction of wear occurs. Therefore, to minimize wear and maximize component life, it is necessary to filter out particles of similar size to the gap.
The recommended levels of fluid contamination and recommended filter accuracy for typical hydraulic components are shown in Table 1.
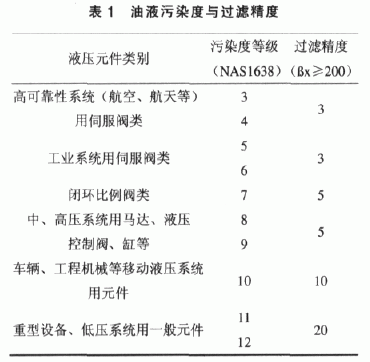
Because hydraulic pollution control technology is still in the development stage in China, many users do not know too much about the definition of filter element filtration accuracy. It is believed that if the system has installed (Xμm) precision filter element, it can ensure that there is no pollution of (Xμm) particles in the system oil. Things, in fact, this is wrong. The national standard GB/T20079-2006 stipulates: The filtration capacity of the filter is expressed by the filtration ratio βx(c), which is defined as: The oil unit volume above and below the filter is larger than a given size x (c The ratio of the number of pollutant particles.
which is:
Xx(c)=Nu/Nd
Where βx (c)—the filter capacity of the filter for particles larger than the size x;
Nu—the number of particles larger than x microns contained in the unit volume of the upstream oil of the filter;
Nd—the number of particles larger than x microns contained in the unit volume of the fluid downstream of the filter;
At present, each filter manufacturer does not stipulate the size of the filtration ratio βx(c). Since the filtration accuracy is determined based on the filtration ratio, the same filtration accuracy is completely different because of the actual βx value. Therefore, (Xμm) filter precision filter can not completely filter particles larger than its accuracy. If the filter is selected to filter less than βx, the degree of oil contamination is also difficult to control.
2 Daily use (maintenance) filter misunderstanding
2.1 Misunderstanding 1: The filter with the bypass valve can not clean or replace the filter element after the filter element is blocked for a long time.
Many users will think that the filter's bypass valve has the same function as the system's safety valve: After the filter element is blocked, the bypass valve is opened, and the system fluid is completely flowed through, which has no effect on the system. This is a misunderstanding. When the bypass valve of the filter is opened, the pollutants (filtered particles that have been filtered out) blocked by the filter will re-enter the system through the bypass valve. At this time, the concentration of the local oil is the highest, and the hydraulic components are extremely Big damage, the previous pollution control will also lose its meaning. Unless the system requires very high continuity of operation, it is best to use a filter without a bypass valve. Even if a filter with a bypass valve is selected, when the filter is contaminated and the transmitter is sent to the transmitter, it is necessary to clean or replace the filter element in time. This is the way to ensure safe and reliable operation of the system.
Fresh Water Chestnut,Organic Fresh Water Chestnut,Frozen Water Chestnut
Chuntian Agricultural Products Co., Ltd. , http://www.km-foods.com