Introduction to the average speed and velocity equation of basic theory of chromatography
First, the average speed
Chromatography, also known as chromatography or chromatography, is a physicochemical analysis method that uses the difference between the forces (distribution, adsorption, ion exchange, etc.) between different solutes (samples) and the stationary phase and mobile phase. When the two phases move relatively, each solute is equilibrated multiple times between the two phases, so that the solute are separated from each other.
That is, when a component of the sample enters the column, a certain distribution is reached in the stationary phase and the mobile phase. The mobile phase always flows at a certain speed, while the stationary phase is stationary. Then the component molecules in the mobile phase will travel forward at the mobile phase flow rate u, while the constituent molecules in the stationary phase will remain with the stationary phase. So what is the average speed of this component?
The components can be separated on the column, meaning that they have different outflow times on the column. We know that the outflow time t = column length L / component average velocity v. The length L of the column is the same for all components, so the key to separation is the different components, and their average speed of movement is different. Why do the average movement speeds of different components differ under the same carrier gas conditions? This tells the internal cause of chromatographic separation: the partition coefficient K of the different components between the stationary phase and the mobile phase is not the same. So what is the external cause of chromatographic separation? Of course there is a relative motion between the mobile phase and the stationary phase.
Since the partition coefficients K of different components are different, the number of molecules in the stationary phase and the mobile phase is different under equilibrium, and the average moving speed is different, so the time they flow out of the column is also There is a difference.
Since chromatographic separation relies on different partition coefficients, we say that the chromatographic separation method is a physical separation method.
Second, the speed equation
The internal factor that chromatographic separation of different components is the difference in partition coefficient K.
What is the distribution coefficient? The partition coefficient is the ratio of the concentrations in the two phases when the substance reaches equilibrium between the two phases. Between the two phases, it does not mean gas, liquid or solid. We use gasoline to extract iodine from water. Water and gasoline are liquid phases, but because they are not miscible, they are also two phases. The partition coefficient is an important physicochemical parameter, which is closely related to the solubility of the components in the two phases. In addition to the composition of the components and the two phases, the influencing factors include temperature and pressure. This pressure is not the external pressure, but the partial pressure of the components. In the case of an ideal gas, the pressure of other gas molecules has no effect on the equilibrium of the components in the two phases. In fact, we often assign the coefficient K as a constant in the case of temperature determination.
In chromatography, the partition coefficient refers specifically to the ratio of the concentration of the component in the stationary phase (s) to the concentration of the mobile phase (m) in equilibrium. We use the s and m feet to represent the two phases, namely:

We know that the average speed of motion is related to the ratio of the number of molecules of the component molecules in the two phases. Although the distribution coefficient K is a constant, it does not fully represent the ratio of the number of molecules in the two phases. The number of molecules, in terms of terms, should be called the distribution ratio k, and also related to the volume of the two phases. which is:
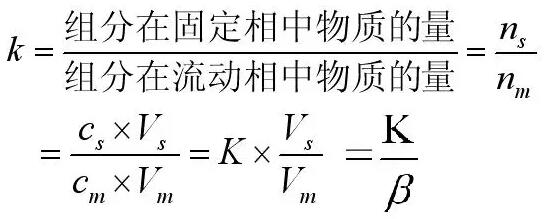
Here we are used to refer to the volume ratio of the mobile phase to the stationary phase as β.
With the concept of allocation ratio k, we can go back and recalculate the average speed of the components. which is:

This formula is a very important formula in the chromatogram, called the velocity equation.
(Content source Hengtianli Instrument Network)
Fireproof Bag ,Fire Proof Bag,Fireproof Pouch,Fire Resistant Bag
Ningbo Zhaomu Electronic Commerce Co., Ltd. , https://www.bofonhome.com