How to control the vine
Grapevines
The healthy tree is the basis for the firming and stable of the grapes. The firming is closely related to the nutrition in the tree. The nutrient in the tree is insufficient, the proportion of incomplete flowers is increased, and the pollen germination rate is low, resulting in poor fruit setting. Falling flowers and falling fruit are also normal physiological phenomena, and excessive fruit drop will result in low fruit setting rate.
The reason why the vine is prosperous
1. Physiological defects: related to the characteristics of the cultivar itself, abnormal ovule development, imperfect pistil or stamen development, or partial pollen sterility, resulting in low fruit setting rate.
2. Climate anomaly: The grape flowering period requires more suitable climatic conditions. The daytime temperature is 20~28°C, the minimum temperature is above 14°C, the relative humidity of the air is about 65%, there are better light conditions, and the climate is abnormal during flowering. Such as low temperature, rainfall, drought and other climatic conditions, directly affecting inflorescence development and growth, the normal pollination and fertilization process can not be completed smoothly, resulting in low fruit set rate.
3. Insufficient nutrient storage of the tree: The nutrients required for the planting of the grape are mainly supplied by the nutrients stored in the stem and root. In the past year, the load is too large or the pests are serious, resulting in poor maturity or early defoliation. Insufficient storage of body nutrients, the new shoots grow weak, the inflorescences are poorly differentiated, the development is not perfect, the flower organs are underdeveloped, leading to flowering and flowering, serious fruit drop after flowering, and low fruit setting rate.
4. Improper distribution of nutrient regulation in the tree: vegetative growth and reproductive growth are carried out before flowering from flowering to flowering. Nutritional growth and reproduction directly compete for nutrients, and the nutrients in this period are mainly derived from nutrients stored in the tree, such as buds and branches. , topping, sub-tip treatment is not timely, waste a lot of tree nutrition, and the tree nutrient distribution is improper, the tree nutrient mainly supplies vegetative growth, and the nutrient deficiency obtained by reproductive growth, the flower organ differentiation is poor, resulting in poor pollination and fertilization , resulting in a large number of falling flowers and fruit, resulting in a low occupancy rate.
5. Inconsistent management technology: smear, fixed branching, topping is not carried out in time, ventilation and poor light transmission, irrigation or spraying pesticides during flowering period, the application of nitrogen fertilizer is more, the new shoots are long, and the pest control is not timely, resulting in low fruit setting rate.
The vine is prosperous and the solution is poor.
1. Control production, reserve nutrition: strictly control the load according to soil fertility, management level, climate, variety and other conditions. To ensure the fruit, the branches are fully and fully mature, the flower buds are well differentiated, and the nutrient accumulation of the tree is sufficient, which can fully meet the demand for nutrients such as growth, flowering, pollination and fertilization.
2. Increase the application of organic fertilizer to improve soil fertility: increase the application of organic fertilizer, timely topdressing, improve soil fertility, ensure a balanced supply of nutrients, and increase the application of organic fertilizer not only can improve soil fertility, but also improve soil aggregate structure for grape growth. Create good environmental conditions, increase the absorption capacity of the root system, and timely irrigate and drain according to weather and soil conditions.
3. Timely germination, branching, topping and treatment of secondary tips: timely germination, branching, reducing nutrient consumption, promoting further development of inflorescence, timely picking, regulating the relationship between vegetative growth and reproductive growth, and making nutrients more by topping Flow to the inflorescence, according to the expected yield, timely remove excess inflorescence, and shape the inflorescence, save nutrients, maximize the demand for nutrients in the inflorescence, ensure the demand for flowering, fertilization and fertilization.
4. Spraying boron fertilizer before flowering: spraying borax solution in the half-month of flowering period to promote pollen tube germination and pollen tube elongation, which has obvious effect on improving fruit setting rate, increasing yield and improving fruit quality.
5. Initial flowering ring stripping: In the flowering stage, the double-edged stripping knife or the bud-jointing knife can be used for ring-stripping at the front part of the fruiting ear about 3 cm or the previous section, which can improve the fruit setting rate.
Disclaimer: Some articles on this website are transferred from the Internet. If legal rights of third parties are involved, please inform this website. phone
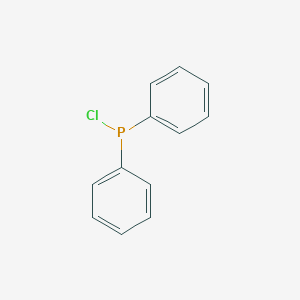
Chlorodiphenylphosphine CAS No.1079-66-9
Chlorodiphenylphosphine Basic Information
Product Name: Chlorodiphenylphosphine
CAS: 1079-66-9
MF: C12H10ClP
MW: 220.63
EINECS: 214-093-2
Mol File: 1079-66-9.mol
Chlorodiphenylphosphine Structure
Melting point 14-16°C
Boiling point 320 °C(lit.)
density 1.229 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
storage temp. Store at R.T.
solubility Miscible with alcohol. Slightly miscible with ammonia.
form Liquid
color Colorless to yellow
Water Solubility Reacts violently
Sensitive Air & Moisture Sensitive
Chlorodiphenylphosphine Application
Chlorodiphenylphosphine is used to introduce the diphenylphosphinyl moiety by aryl ortho-lithiation. It is also used as an intermediate to make antioxidants, flame retardants, stabilizers, Catalysts, photoinitiators, and optical brighteners. Used as a halogenation reagent for the conversion of alcohols into halides, in the preparation of solid-phase reagent for the conversion of alcohols to alkyl halides.
Chlorodiphenylphosphine,Chlorodiphenylphosphine Oxide,Chlorodiphenylphosphine 31P Nmr,Chlorodiphenylphosphine Synthesis
Shandong YingLang Chemical Co.,Ltd , https://www.sdylhgtrade.com