Climbing effect in the viscosity measurement (encapsulation effect)? How to deal with
The climbing rod effect is one of the manifestations of high viscoelasticity of the polymer. For the viscous fluid, due to centrifugal force, the liquid level will show a concave shape (left); different viscous fluid, filled in a container of liquid polymer (viscoelastic fluid), when such sample is placed into the rotor rotates, There is no nearing the wall of the container due to inertia, but instead around the rod, there is a phenomenon of " climbing rod " climbing up the rod (right). This phenomenon is called the Weissenberg effect, and the normal stress effect is also called " Package axis " effect.
The reason for this phenomenon is that a polymer material having elasticity, since a polymer forming an anisotropic structure in the fluid flow generated by: an elastic macromolecular chains during rotation will occur along the circumferentially oriented and pull Stretching deformation, resulting in pressure toward the axis, the closer the off-axis is, the greater the shear rate, so the greater the normal stress, the greater the elastic restoring force of the polymer chain , so that the liquid along the axis When it is squeezed upwards, there is a phenomenon of climbing.
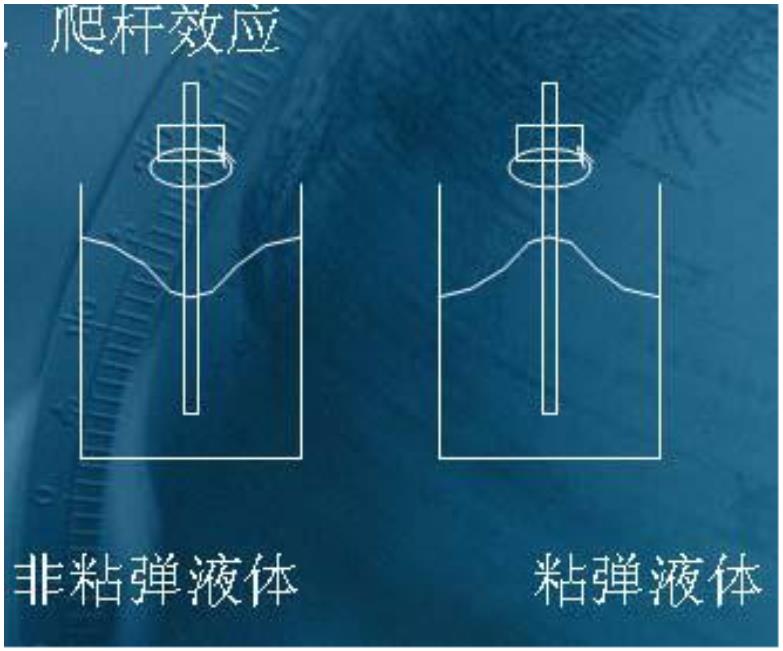 What is a viscoelastic fluid? It has the characteristics of viscous liquid and elastic solid.
What is a viscoelastic fluid? It has the characteristics of viscous liquid and elastic solid.
Viscous liquid: stress, flow, and permanent deformation
Elastic solid: stress, deformation, removal of external force, deformation recovery
Viscoelastic fluid: Deformation occurs when force is applied, external force is removed, deformation is partially recovered, and the longer the force is applied, the less the deformation recovery portion is .
The unfavorable consequences of the climbing rod effect and its solutions:
1 , Â The creeping effect is normal for polymer solutions, as long as the molecular weight reaches a certain number, it is necessary to climb, which is also high.
The embodiment of the flexibility of the molecular solution. When using a common viscometer to measure the sticking phenomenon, the data obtained is often larger than the actual viscosity value, and the material is actually pseudoplastic shear thinning, so the characteristics of such materials often make the tester feel To the confusion.
2 , Â To overcome the climbing effect:
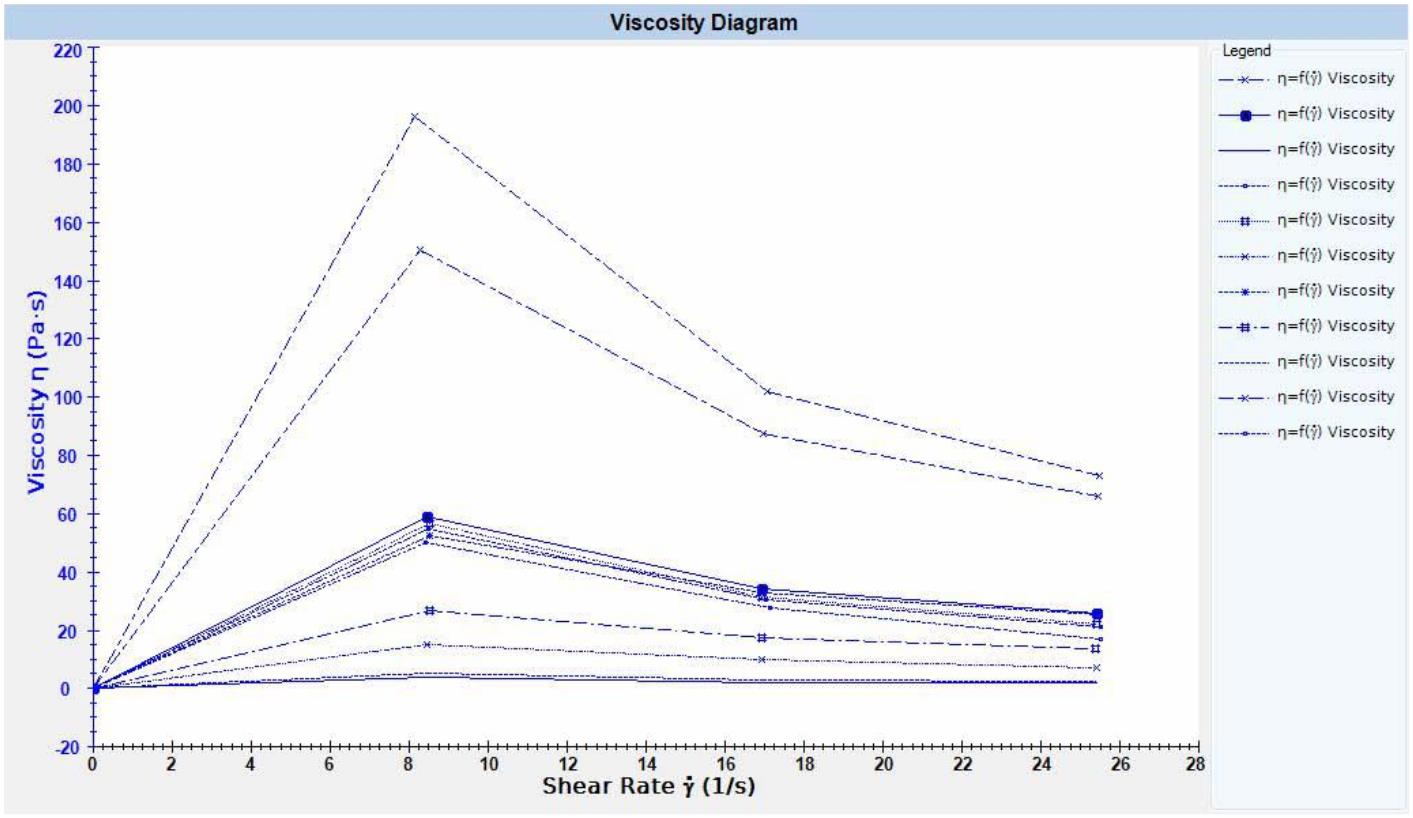
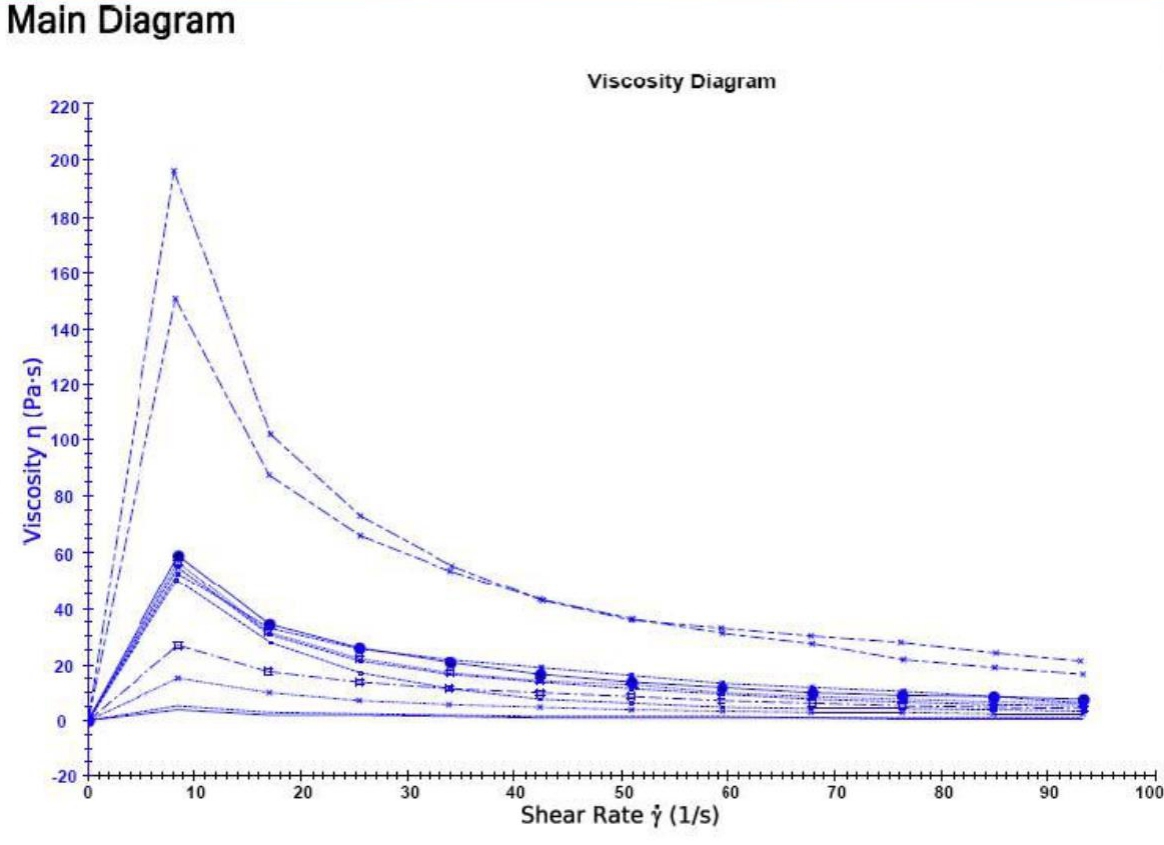
For such materials, coaxial cylindrical rotors cannot be used. The simple method of zui is to adopt  RST-CPS  Cone and plate rheometer, according to the viscosity range of the material  CP25-1  or  CP50-1  The rotor, the shear rate can do first scanning, the basic rheological curve, then the measurement condition is determined according to the situation zui generally recommend a low shear rate measurement. As shown below, a polymeric rheology curves under different polymerization conditions. From the curve, it can be found that the material is a pseudoplastic fluid, and it has been found to have thixotropy after experimentation , and the zui is determined at a lower shear rate (the sample is used  8  Measurement under the conditions of S-1 ),
Obtaining a stable and reliable viscosity value provides reliable experimental data for the determination of the production process.
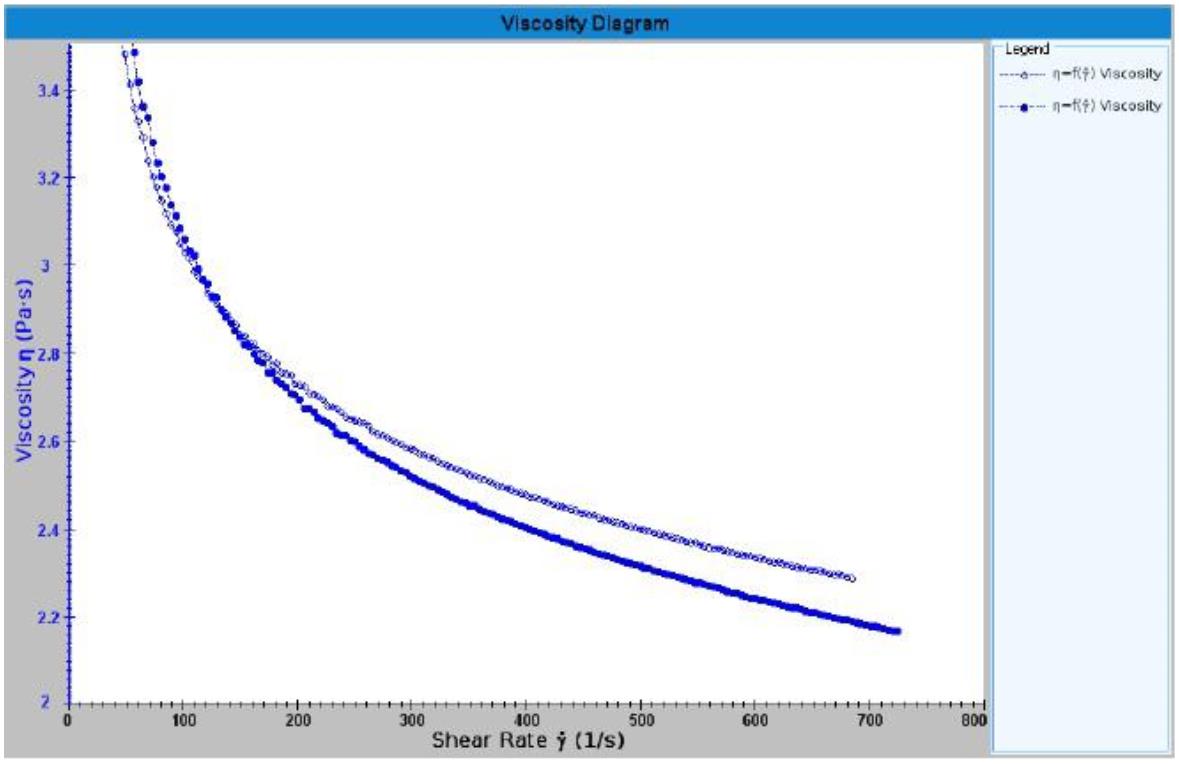
For viscoelastic gels or sample (polymer high degree of polymerization, high concentration), a cone-plate rheometer continuously increasing and decreasing linear stress and shear rate by the method of sample can be limited to some extent The elastic response of the internal structure causes inconsistencies in the data , so use  RST  More suitable rheometer testing the sample, the specific measurement conditions: scan can be adopted for testing the shear rate flow curve, or choose a relatively low shear rates (0-20  S-1 ) Perform a measurement for a period of time and then take the average.
The results are very different (the user sample shows splashing, and the foreign sample can be produced normally).
?
Â
Centrifuge Products,High-Speed Centrifuge,Refrigerated Centrifuge For Lab,Medical Low Speed Centrifuge
Guangdong Widinlsa International Co.Ltd , https://www.gzwidinlsa.com