Application of Near Infrared Fluorescence Labeling in Tumor Optical Imaging
Author: Bai Huimin
Background: Fluoride 18-labeled glucose (FDG) has been used in clinical detection, staging, and therapeutic surveillance of tumors and other diseases. However, its radioactive side effects have always plagued patients, and recent non-radioactive markers have emerged. The near-infrared drug is gradually accepted by doctors and patients because of its non-toxicity, convenient labeling and economical benefits. The article presented below mainly uses the tumor imaging of a near-infrared-labeled deoxyglucose analog as an example to explain the advantages and disadvantages of near-infrared imaging technology.
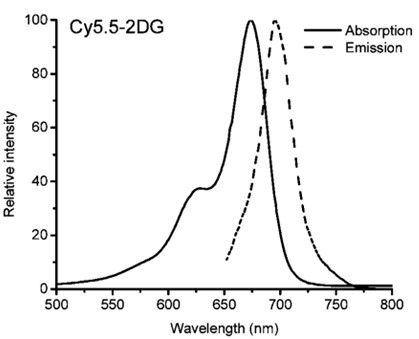
Partial results: near-infrared imaging of malignant gliomas implanted subcutaneously
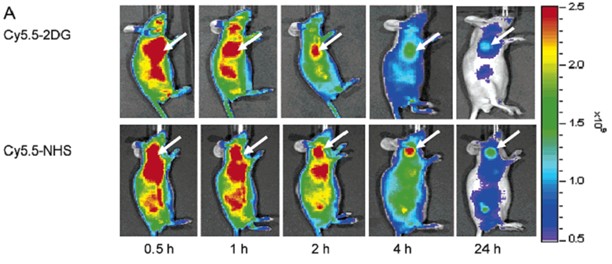
The two dyes were intravenously injected into the nude mouse tumor model, and the results of multiple phases indicated that both substances were higher than the normal tissue at the tumor site (shown by the white arrow).
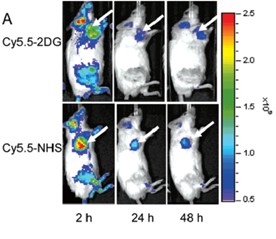
The same result appears in the near-infrared imaging results of melanoma:
Discussion: In previous reports, 2-NBDG can enter living cells via the glucose transport system (GLUT) and can be aggregated in malignant tumor cell lines such as breast cancer cells MCF-7, hepatoma cells HepG2. In the results of this study, it was also shown that 2-NBDG accumulates in the cytoplasm of U87MG cells, and that near-infrared-labeled Cy5.5-2DG can enter many tumor cell lines. For example: C6, A75M, B16F0, MDA-MB-435 (results not shown), and because the emission spectrum of 2-NBDG is at 475nm, it is not suitable for animal imaging, which limits its clinical and preclinical applications, near-infrared labeling. Greatly improved its physical properties in optical imaging.
Summary: Near-infrared imaging is an effective means of preclinical and clinical diagnosis of diseases, and real-time surgical guidance, and attracts the attention of many scientific research and medical personnel. Its non-invasive, non-radioactive, non-toxic characteristics make it It has great application potential and value before clinical and clinical. This article aims to develop optical probes suitable for near-infrared tumor-specific imaging, and the ease of labeling of most near-infrared dyes has also facilitated the development of this field.
With the development of technology, static imaging has been unable to meet the needs of scientific research and surgery. Near-infrared real-time imaging has become the new darling of the optical imaging industry. The Fluobeam series produced by Fluoptics is a high sensitivity (detectable picomolar level ( 10 -12 ) Even the flying-molar (10 -15 ) fluorescent signal) The first hand-held open real-time imaging system enables compatible imaging of large animals and small animals on the same instrument; experimental preclinical experiments and The perfect combination of real-time guidance in clinical surgery.
ANTIBIOTIC
Antibiotics refer to a class of secondary metabolites produced by
microorganisms (including bacteria, fungi, actinomycetes) or higher
animals and plants in the process of life, which can interfere with the
development of other living cells. Clinical commonly used antibiotics
include extracts from microbial culture medium and compounds synthesized
or semi synthesized by chemical methods.
The antibacterial or bactericidal effects of antibiotics and other
antimicrobial agents are mainly aimed at the mechanism of "bacteria exist
but human (or other animals and plants) do not", including four major
mechanisms: inhibition of bacterial cell wall synthesis, enhancement of
bacterial cell membrane permeability, interference with bacterial protein
synthesis and inhibition of bacterial nucleic acid replication and
transcription.
Our business covers Africa, the Middle East, Central Asia and Southeast Asia.
North Africa Egypt, Libya, Tunisia, Morocco, Algeria.
East Africa is Ethiopia, Somalia, Kenya, Tanzania, Uganda, Burundi, Rwanda and Seychelles.
West Africa usually includes Mauritania, Senegal, Gambia, Mali, Burkina Faso, Guinea, Guinea Bissau, Cape Verde, Sierra Leone, Liberia, C ô te d'Ivoire, Ghana, Togo, Benin, Niger, Nigeria, etc.
South Africa is South Africa, including Zambia, Malawi, Zimbabwe, Botswana, Swaziland, Lesotho, Mozambique, Republic of South Africa, Namibia, Madagascar, Comoros, Mauritius, Reunion Island, France, St. Helena and ascension.
Central Africa includes the Central African Republic, Chad, Cameroon, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, the Republic of Congo, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Sao Tome and Principe.
Central Asia refers to the inland region of Central Asia: Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan and Afghanistan.
Southeast Asia: Myanmar, Thailand, Cambodia, Laos, Vietnam, Philippines, Malaysia, Singapore, Brunei, Indonesia and Timor Leste.
Countries and regions in West Asia include Saudi Arabia, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, UAE, Oman, Qatar, Bahrain, Turkey, Israel, Palestine, Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, Yemen, Cyprus, Georgia, Armenia and Azerbaijan.
North African countries and regions include Egypt, Libya, Tunisia, Algeria, Morocco, Madeira Islands, Azores Islands and Western Sahara.
Animal use antibiotic medicine to Africa,Veterinary antibiotics to Middle East,Antibacterials for animals to Southeast Asia
Shandong Unovet Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd. , https://www.unovetcn.com


